UNDERSTANDING ABOUT ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT
The necessity of treating wastewater
Treating wastewater is crucial for several reasons:
- Public Health Protection: Wastewater contains bacteria, viruses, and parasites that can cause diseases. Treating wastewater eliminates or reduces these pathogens, protecting public health by preventing the spread of waterborne diseases.
- Environmental Protection: Untreated wastewater can harm aquatic ecosystems by depleting oxygen levels in water bodies, which can kill fish and other aquatic life. Treatment reduces pollutants and helps maintain the ecological balance of rivers, lakes, and seas.
- Water Reuse: Treated wastewater can be reused for various purposes, including irrigation, industrial processes, and even as potable water after advanced treatment. This reduces the pressure on freshwater resources, especially in water-scarce areas.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many regions have strict regulations regarding the discharge of wastewater into the environment. Treating wastewater ensures compliance with these regulations, helping avoid legal penalties and fines.
- Economic Benefits: Proper wastewater treatment can lead to the recovery of valuable resources, such as biogas, which can be used to generate energy, or nutrients for use as fertilizer. This can provide economic benefits and contribute to a circular economy.
- Community Well-being and Aesthetics: Treating wastewater helps prevent the pollution of water bodies, which can have a positive impact on the quality of life in communities, enhance recreational activities, and improve the aesthetics of natural water bodies.
In summary, wastewater treatment is essential for protecting public health, preserving the environment, conserving water resources, ensuring regulatory compliance, realizing economic benefits, and improving community well-being and the natural landscape.
See what Green Valley can help you with wastewater treatment
- Green Valley specializes in providing cutting-edge wastewater treatment solutions, leveraging advanced technologies to meet the environmental and regulatory demands of various industries.
- With a focus on sustainability and efficiency, Green Valley offers customized solutions, including Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) systems, Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) technology, and Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs), to optimize wastewater treatment processes.
- By integrating these advanced technologies, Green Valley can help your company achieve significant reductions in pollutants, meet stringent discharge standards, and facilitate water reuse initiatives. Our expertise in nutrient removal and anaerobic digestion also supports waste minimization and energy recovery, contributing to circular economy goals.
- Partnering with Green Valley ensures compliance with environmental regulations, enhances your company's sustainability profile, and leads to long-term operational benefits.
Contact us now!
_____________________
+84 988 463 742 (Zalo, Whatsapp)
stephen@greenvalleyjsc.com
See our Wastewater Treatment Plant projects!
Current regulations for wastewater treatment and management
- In Vietnam, regulations for wastewater treatment and discharge are governed by a comprehensive set of laws and decrees aimed at minimizing environmental impact and promoting sustainable water resource management. The government has been updating these regulations to address the challenges posed by industrialization and urbanization.The latest amendment to Vietnam's environmental legislation occurred on January 1, 2022, when the.
- Environmental Protection Law 2020 (code
72/2020/QH14) superseded the previous Environmental Protection Law 2014 (code 55/2014/QH13).
- Recent efforts include the drafting of new industrial wastewater standards, indicating a move towards more stringent controls and monitoring of industrial wastewater contaminants. Companies are required to report any changes in the contaminants that are subject to periodic measurement, reflecting an emphasis on adaptability and responsiveness to new environmental challenges.
- Decree 45, issued in 2022, outlines sanctions for environmental violations, including those related to wastewater management. It establishes a range of penalties, from warnings to fines and additional sanctions such as the suspension of operations and revocation of environmental licenses for non-compliance with wastewater discharge regulations. The decree aims to enforce compliance with environmental standards and promote responsible wastewater management among businesses and individuals.
- The general requirements for wastewater management in Vietnam, as outlined in
Decree 08/2022/ND-CP, emphasize the prevention, minimization, collection, transport, reuse, recycling, and treatment of wastewater. These regulations mandate the efficient use of water resources and the reduction of adverse environmental impacts. They also prescribe a prioritized approach to wastewater management, including treatment for reuse in production and services, and the treatment and discharge of wastewater in accordance with environmental technical regulations.
- These regulations demonstrate Vietnam's commitment to improving wastewater management practices, reducing environmental pollution, and ensuring sustainable water use and protection.
Conventional Wastewater treatment technologies
In the context of conventional wastewater treatment technologies, the process typically involves several advanced stages:
01
Primary treatment
- This stage primarily involves mechanical processes to remove gross solids and floating materials.
- Techniques include screening to exclude large debris and grit chambers to sediment inert dense particles.
- However, this stage generally does not involve biological treatment units like anoxic or anaerobic tanks.
02
Secondary treatment
- This phase is where biological processes predominantly occur to degrade soluble organic matter and suspended solids.
- It includes aerobic processes in activated sludge systems, where microorganisms convert organic materials into biomass.
- An anoxic tank may be employed for denitrification, where nitrate is reduced to nitrogen gas, thus removing nitrogen from the wastewater.
- Additionally, nitrification can occur in aerobic conditions, converting ammonia to nitrate, often in a separate reactor or designated zone within the treatment plant.
03
Tertiary treatment
- This advanced treatment stage is designed to further polish the effluent quality before discharge or reuse.
- It often includes processes like filtration through sand or activated carbon filters to remove residual particulate matter and nutrient removal processes, where additional biological treatment in anoxic tanks can further reduce nitrogen compounds through denitrification.
- Disinfection, commonly through chlorination or ultraviolet (UV) light, ensures the elimination of pathogenic organisms.
04
Sludge treatment
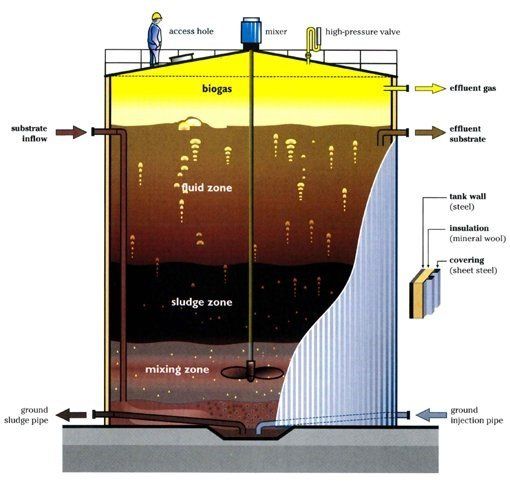
- The byproduct of primary and secondary treatment is sludge, which undergoes processes like thickening and anaerobic digestion.
- In the anaerobic digester, microorganisms break down organic matter in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas and reducing the volume of sludge.
- Following digestion, dewatering processes, such as centrifugation or filter presses, concentrate the sludge solids, preparing them for disposal or beneficial use.
Advanced wastewater treatment technologies
Advanced technologies in wastewater treatment have been developed to address limitations of conventional methods and to meet more stringent environmental standards. Here are some of the advanced technologies used in wastewater treatment:
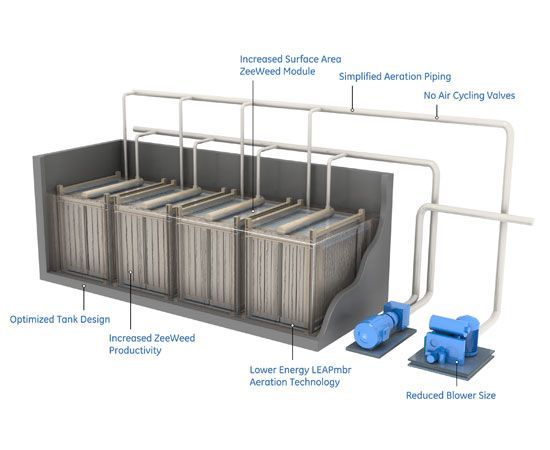
- Membrane Bioreactors (MBR): MBR technology combines conventional biological treatment processes with membrane filtration. It provides high-quality effluent by integrating activated sludge treatment with a membrane filtration unit, which replaces the secondary settling tank. The membranes are usually ultrafiltration or microfiltration units that retain biomass and suspended solids, producing clear and high-quality effluent.
- Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR): This system uses thousands of polyethylene biofilm carriers operating in mixed motion within an aerated wastewater treatment basin. MBBR technology provides a protected surface area to support the growth of biofilm, which consumes organic matter in the wastewater. It's efficient for nitrification and can be used in both municipal and industrial wastewater treatment.
- Reverse Osmosis (RO): RO is a membrane process that removes a wide range of contaminants from water by passing it through a semi-permeable membrane. It is particularly effective in removing salts, microorganisms, and organic molecules, making it suitable for producing high-quality effluent and for applications requiring water reuse.
- Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs): These processes involve the generation of highly reactive species like hydroxyl radicals that can degrade a wide range of organic pollutants and pathogens in wastewater. AOPs, including ozone, hydrogen peroxide, and ultraviolet light, are used to break down pollutants that are difficult to treat by conventional biological processes.
- Nutrient Removal Technologies: Advanced nutrient removal technologies, such as enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) and denitrification, are used to remove excess nutrients (phosphorus and nitrogen) from wastewater. These processes are crucial for preventing eutrophication in water bodies.
- Anaerobic Digestion for Sludge Treatment: This process treats sludge produced during wastewater treatment to reduce volume and produce biogas, a renewable energy source. Anaerobic digestion is effective in breaking down organic material in the absence of oxygen, converting it into methane and carbon dioxide.
These advanced technologies enhance the efficiency of wastewater treatment processes, enabling higher levels of contaminant removal, resource recovery, and water reuse, contributing to sustainable water management practices.